Hot Topics
Vol. 59, No. 11, November(2010)
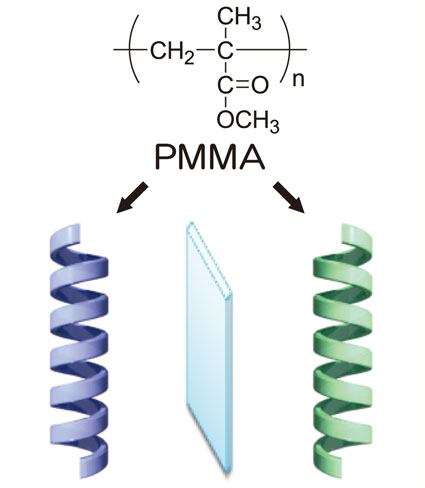
| Optically Active PMMA Takehiro KAWAUCHI Department of Environmental and Life Sciences, Toyohashi University of Technology |
||
|
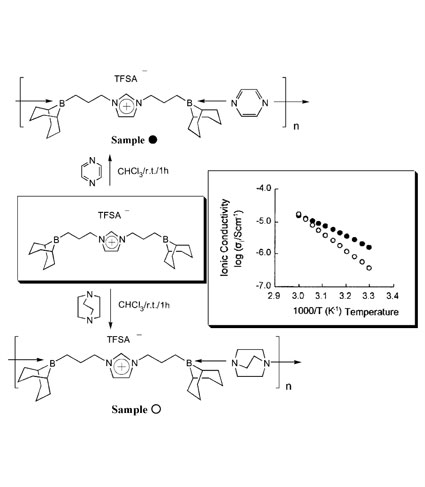
| Synthesis of Supramolecular Solid Polymer Electrolytes via Self-assembly of a Diborylated Ionic Liquid Noriyoshi MATSUMI, Akihito KAGATA, and Keigo AOI Graduate School of Bioagricultural Sciences, Nagoya University |
||
|
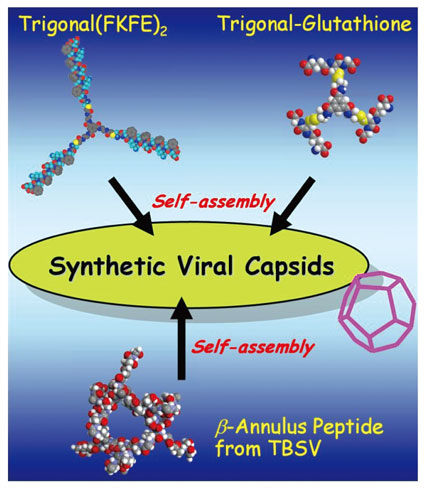
| Toward Creation of Synthetic Viral Capsids Kazunori MATSUURA Department of Applied Chemistry, Kyushu University |
||
|
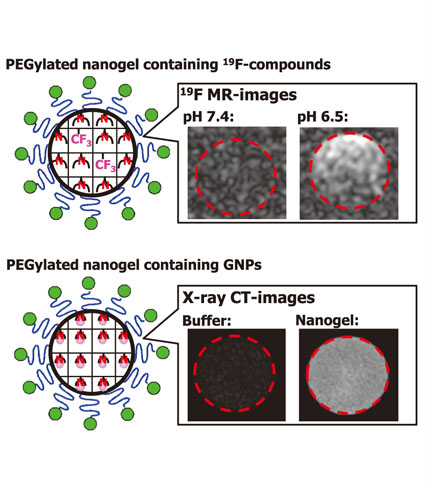
| Smart PEGylated Nanogels for Pinpoint Nano-Imaging Motoi OISHI Graduate School of Pure and Applied Sciences, University of Tsukuba |
||
|
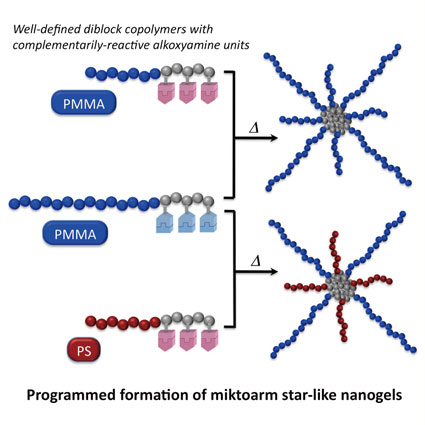
| Dynamic Covalent Approach to Macromolecular Design of Reactive Polymers Hideyuki OTSUKA Institute for Materials Chemistry and Engineering, Kyushu University |
||
|
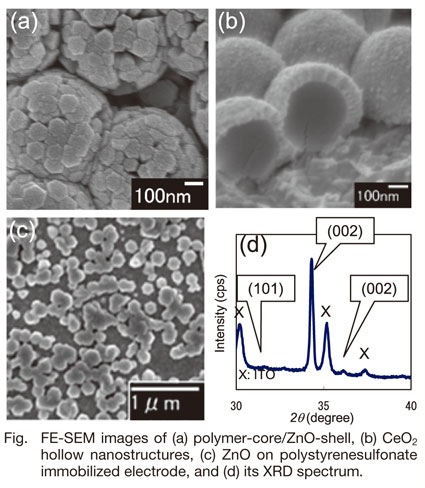
| Interaction between Polymer Surface and Electrodeposited Inorganic Oxides Mitsuru WATANABE Osaka Municipal Technical Research Institute |
||
|
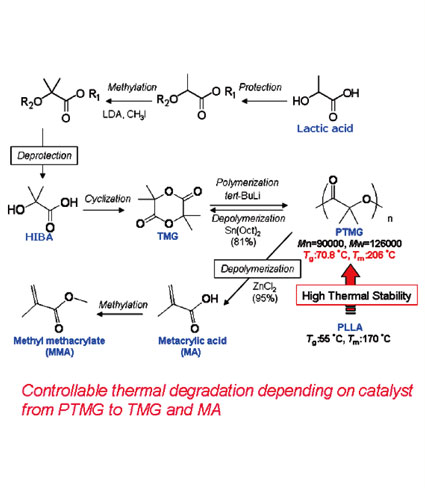
| Development of Polytetramethylglycolide from Lactic Acid for Sustainable Biomass-Based Polyester Yoshito ANDOU1, Yoshihito SHIRAI1,2, and Haruo NISHIDA1 1Eco-Town Collaborative R&D Center for the Environment and Recycling, Kyushu Institute of Technology. 2Department of Biological Functions and Engineering, Kyushu Institute of Technology |
||
|
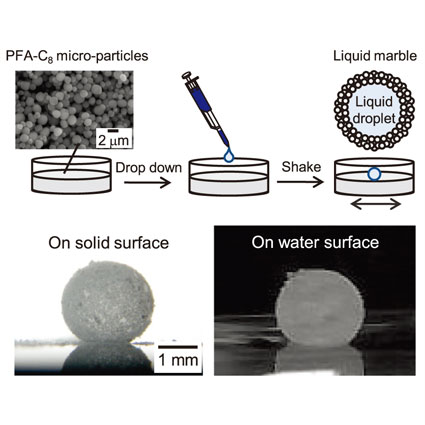
| Encapsulation of Liquid Droplets with Hydrophobic Polymer Micro-particles Daisuke MATSUKUMA, Hirohmi WATANABE, and Atsushi TAKAHARA JST, ERATO, Takahara Soft Interfaces Project |
||
|
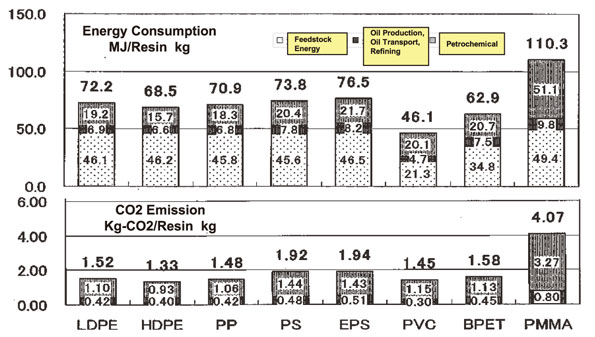
| Study on Life Cycle Inventory (LCI) Data of Commodity Resins Hajime NISHIHARA Technology Research & Development Department, Plastic Waste Management Institute |
||
|