Hot Topics
Vol. 60, No. 1, January(2011)
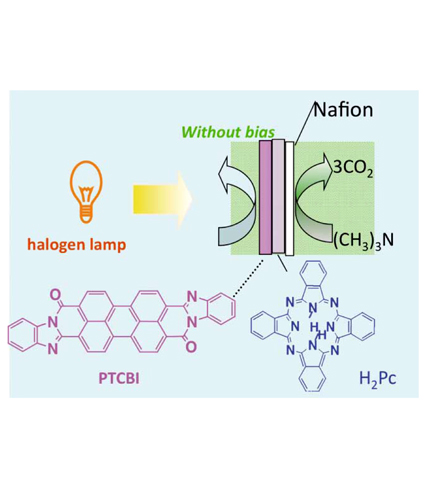
| Degradation of Organic Compounds Using an Organophotocatalyst with p-n Junction Responsive to the Whole Spectrum of Visible Light Keiji NAGAI Division of Integrated Molecular Engineering, Chemical Resources Laboratory, Tokyo Institute of Technology |
||
|
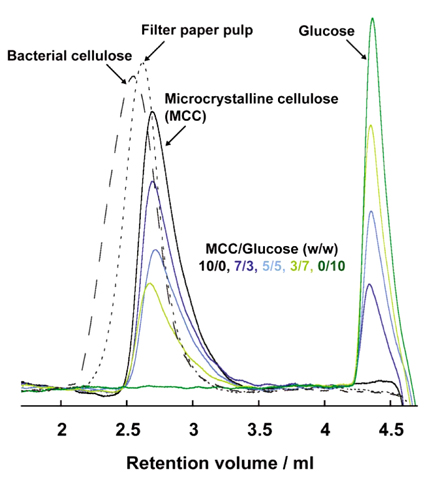
| High Performance Ionic Liquid Chromatography Yukinobu FUKAYA Department of Biotechnology, Tokyo University of Agriculture & Technology |
||
|
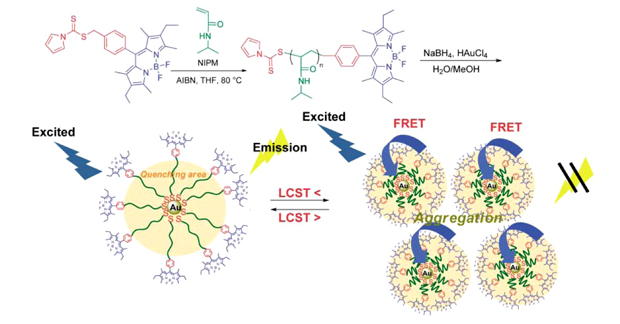
| Reversibly Thermoswitchable Luminescent Gold Nanoparticle Stabilized by a BODIPY-Terminated Water-Soluble Polymer Atsushi NAGAI, Ryousuke YOSHII, Takeshi OTSUKA, Kenta KOKADO, and Yoshiki CHUJO Department of Polymer Chemistry, Graduate School of Engineering, Kyoto University |
||
|
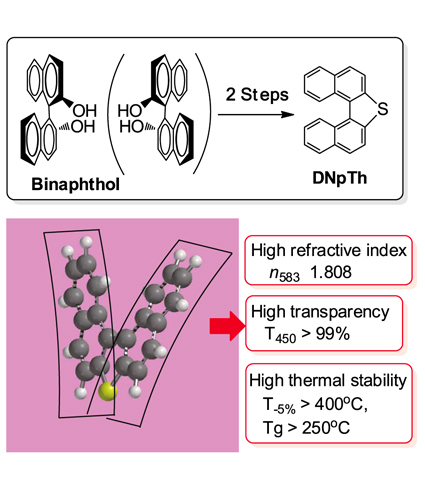
| Dinaphthothiophene: A Novel High Refractive Index Material with High Thermal Stability Yoko NAMBU Institute of Technological Research, Kanagawa University, and Department of Material and Life Chemistry, Faculty of Engineering, Kanagawa University |
||
|
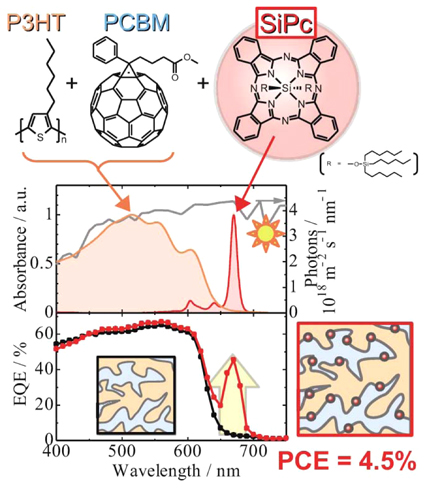
| Dye-Sensitized Polymer/Fullerene Solar Cells Satoshi HONDA1, Hideo OHKITA1,2, Hiroaki BENTEN1, and Shinzaburo ITO1 1Graduate School of Engineering, Kyoto University, 2PRESTO, Japan Science Technology Agency |
||
|
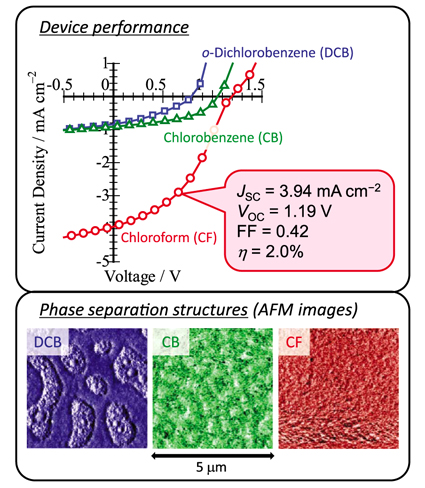
| Highly Efficient All-Polymer Solar Cells Daisuke MORI1, Hiroaki BENTEN1, Hideo OHKITA1,2, Shinzaburo ITO1, and Kunihito MIYAKE3 1Graduate School of Engineering, Kyoto University, 2PRESTO, Japan Science Technology Agency, 3Sumitomo Chemical, Co., Ltd. |
||
|
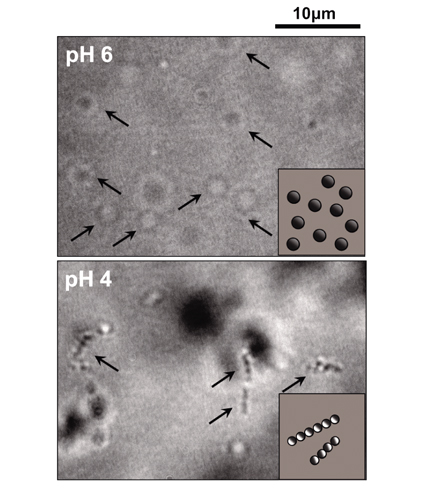
| Janus Hydrogel Particles Daisuke SUZUKI International Young Researchers Empowerment Center, Shinshu University |
||
|
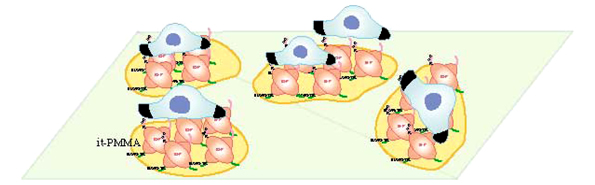
| Design of an Artificial Extracellular Matrix Protein with PMMA Binding Function Naoki TANAKA Department of Biomolecular Engineering, Kyoto Institute of Technology |
||
|
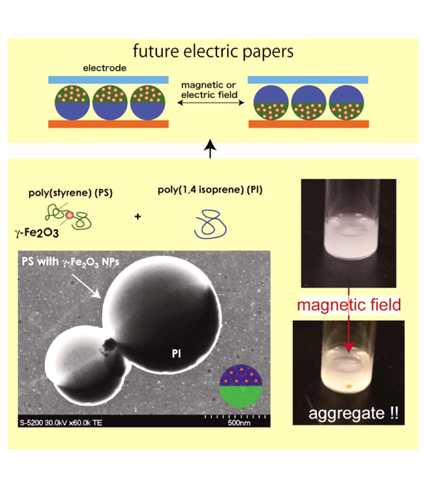
| Magneto-anisotropic Janus Particles Containing γ-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles Hiroshi YABU1,2 and Toshihiko ARITA1 1Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials (IMRAM), Tohoku University 2Precursory Research for Embryonic Science and Technology (PRESTO), Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) |
||
|