Hot Topics
Vol. 61, No. 2, February (2012)
|
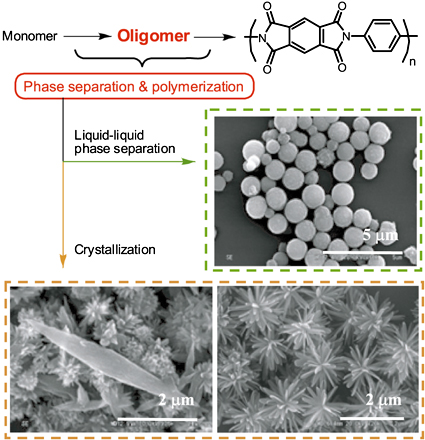
Morphology Control of Aromatic Polymers Using Phase Separation during Polycondensation
Kunio KIMURA Graduate School of Environmental Science, Okayama University |
||
|
|
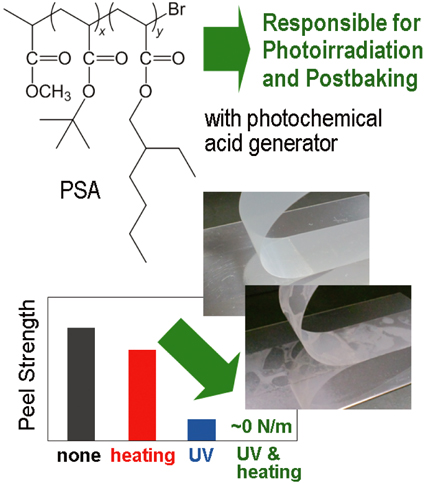
Dismantlable Adhesion Using Acrylic Block Copolymers for On-Demand Debonding
Akikazu MATSUMOTO Department of Applied Chemistry and Bioengineering, Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka City University |
||
|
|
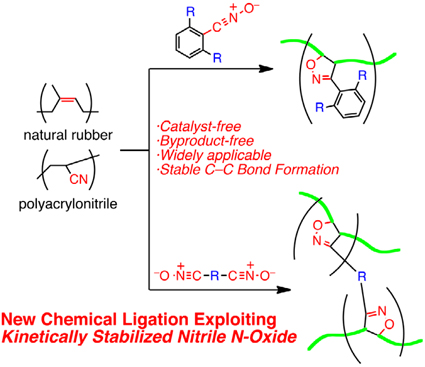
Stable Nitrile N-Oxide Chemistry: A New Chemical Ligation Tool to Common Polymers
Yasuhito KOYAMA*, Morio YONEKAWA, Kaori MIURA, Tohru MATSUMURA, and Toshikazu TAKATA Department of Organic and Polymeric Materials, Tokyo Institute of Technology |
||
|
|
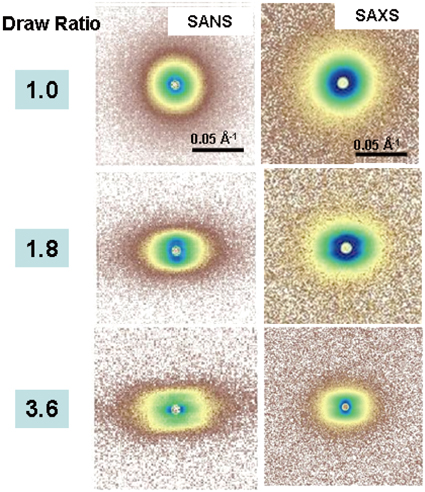
Shish-Kebab Formation Process of Polyethylene During Uni-Axial Draw with Small-Angle X-Ray and Neutron Scattering Measurements Go MATSUBA Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Yamagata University |
||
|
|
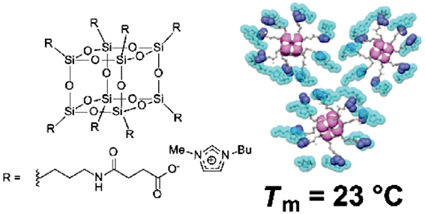
Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids Based on POSS
Kazuo TANAKA* and Yoshiki CHUJO Department of Polymer Chemistry, Graduate School of Engineering, Kyoto University |
||
|
|
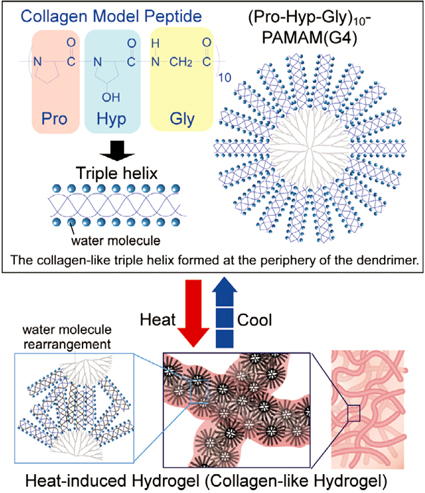
Temperature-induced Hydrogel Based on Collagen-mimic Dendrimers
Chie KOJIMA Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Research Center, Research Organization for the 21st Century, Osaka Prefecture University |
|
|