Hot Topics
Vol. 61, No. 3, March (2012)
|
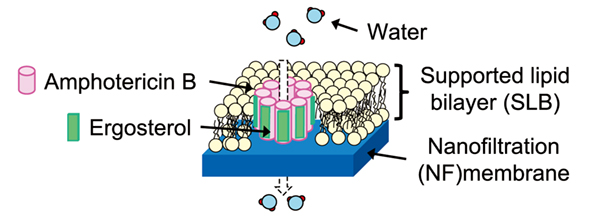
Preparation of biomimetic membrane for reverse osmosis process using supported lipid bilayer
Hideto MATSUYAMA Center for Membrane and Film Technology, Kobe University |
||
|
|
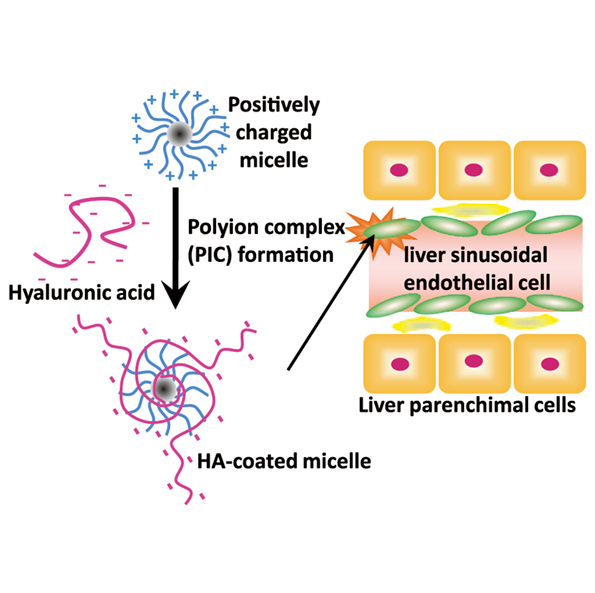
Highly stable polymeric micelles
Yuichi OHYA Faculty of Chemistry, Materials and Bioengineering, Kansai University |
||
|
|
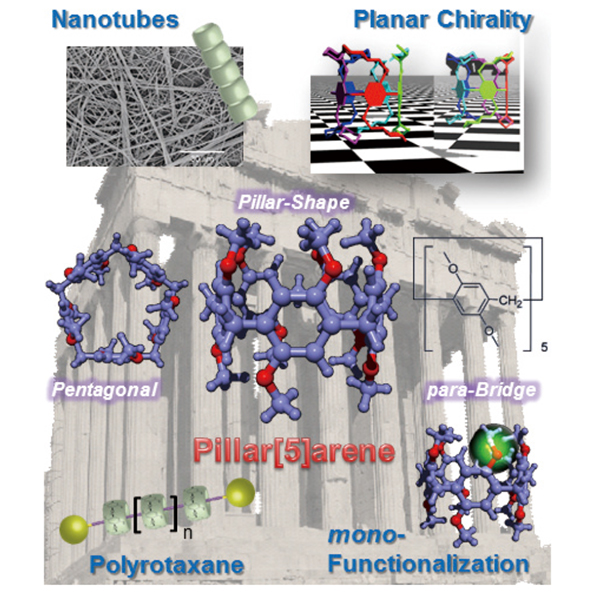
Synthesis of Novel Macrocyclic Hosts メPillar[5]areneモ and Their Application for Supramolecular Materials
Tomoki OGOSHI Department of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Graduate School of Natural Science and Technology, Kanazawa University |
||
|
|
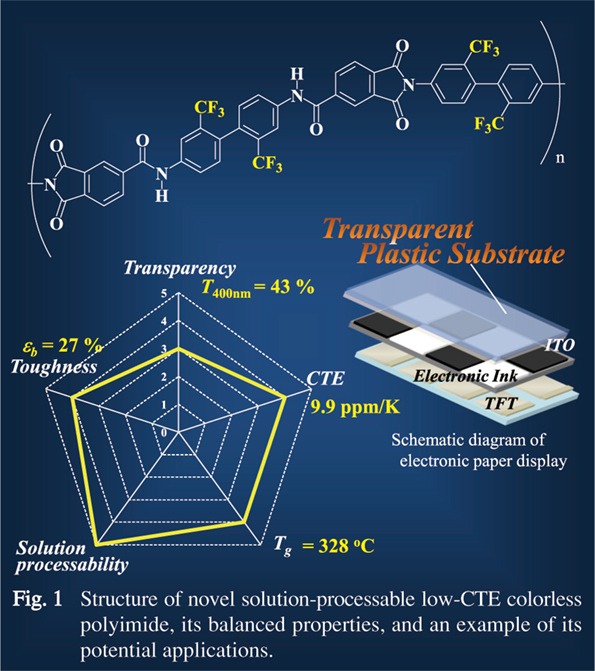
In-plane Orientation in Colorless Polyimides as Induced by Solution Casting from Polyimide Varnishes (6). Applications to Low-CTE and Transparent Plastic Substrates Tomohiro ISHIGAMI, Junichi ISHII, and Masatoshi HASEGAWA Faculty of Science, Toho University |
||
|
|
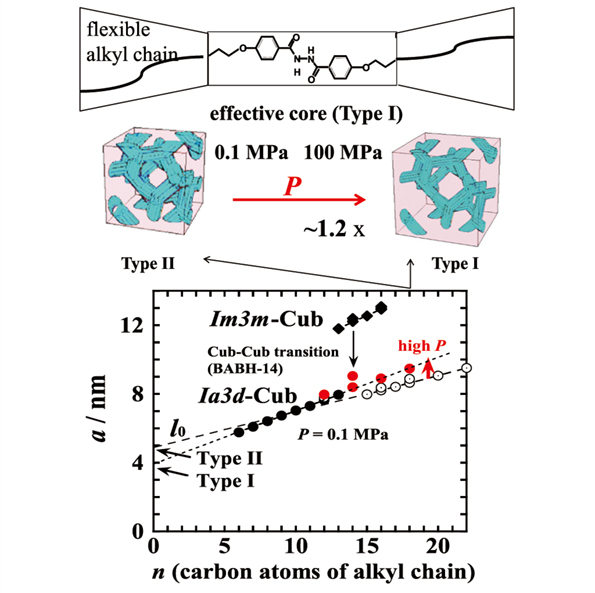
Expansion of Ia3d Cubic Lattice under Pressure
Yoji MAEDA1, Shoichi KUTSUMIZU2, and Shinichi SAKURAI3 1Department of Life Science and Sustainable Chemistry, Tokyo Polytechnic University 3Department of Chemistry, Gifu University 3Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Kyoto Institute of Technology |
||
|
|
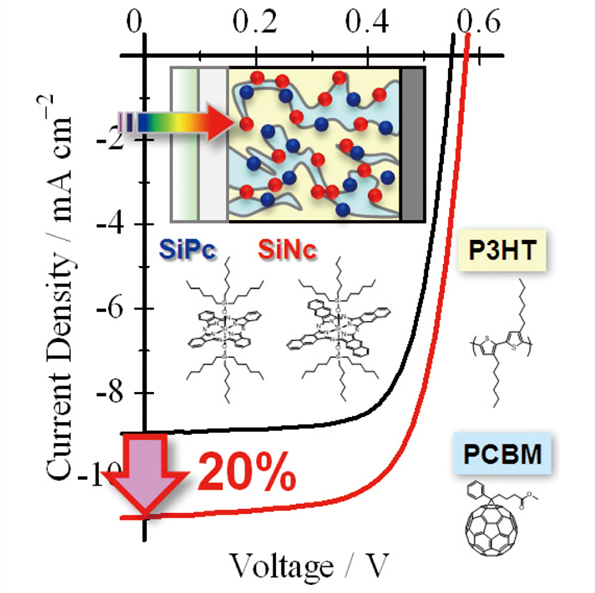
Multi-Colored Dye Sensitization of Polymer/Fullerene Solar Cells
Hideo OHKITA1,2, Satoshi HONDA1, Hiroaki BENTEN1, and Shinzaburo ITO1 1Graduate School of Engineering, Kyoto University 2Japan Science and Technology Agency, PRESTO |
|
|