|
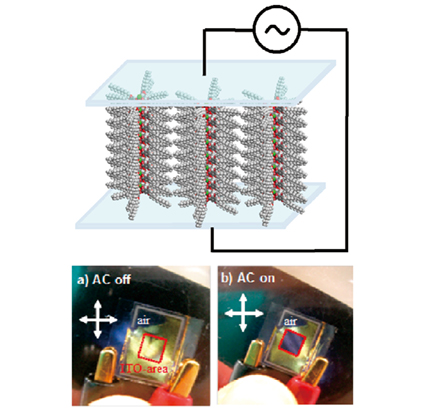
The ability to self-assemble coordination nanoarchitectures holds promise to tailor and improve their functions for technologically important applications. We developed supramolecular covering techniques to convert solid-state one- dimensional coordination compounds into lipophilic, soluble nanowires. They show unique characteristics such as thermochromism, solvatochromism and spin conversion in organic media, which are controlled based on self-assembly. Macroscopic orientation of these coordination molecular wires can also be controlled by using electrophoretic orientation techniques, as recently demonstrated for lyotropic liquid crystals of halogen-bridged diruthenium complexes in decane. Self-assembly of coordination networks has been also demonstrated in aqueous environments. Upon mixing nucleotides and lanthanide ions in water, amorphous coordination nanoparticles are spontaneously formed. These coordination networks revealed adaptive inclusion of functional molecules such as dyes, porphyrins and even inorganic nanoparticles. These unique features provide opportunities to design functional molecular systems.
Polymer Preprints, Japan 2012, 61, 47.
|